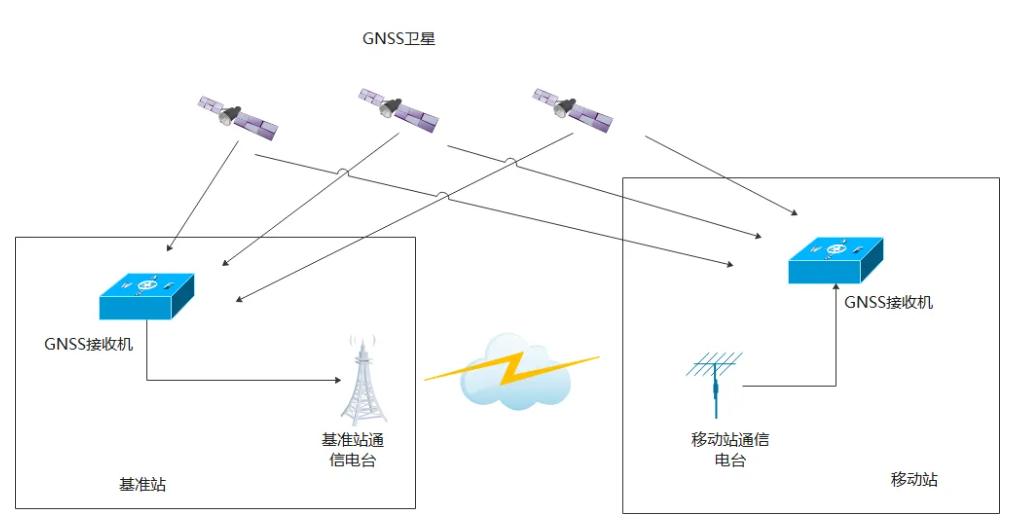
Conventional single reference station differential positioning
The conventional single-base differential positioning system consists of two components: the base station and the mobile station. Both the base station and the mobile station are equipped with multi-system multi-frequency GNSS satellite receivers and communication radios. The process of conventional differential positioning is generally as follows:
The base station is generally located at a fixed position on the ground, and the position is the precise position coordinates obtained through geodetic measurement. The GNSS receiver in the base station receives GNSS satellite signals (currently the world's four major satellite navigation systems: GPS, Beidou, Galileo and GLONASS satellites, etc.), and sends the observation information of each satellite (the observation information includes the satellite number, pseudorange, carrier phase, Doppler, signal-to-noise ratio, etc.) to the communication radio of the base station at a certain frequency.
Since the base station is generally fixed and the satellite observation changes very little in a short period of time, the observation information of the base station can generally be updated and sent once per second.
The communication radio of the base station transmits the observation information through the wireless communication link.
If the mobile station is within the coverage of the base station's communication radio, the communication radio on the mobile station can receive the observation information of the base station and send the observation information to the mobile station's GNSS receiver;
The GNSS receiver in the mobile station receives the observation information from the base station, uses the differential positioning principle, eliminates the error, and calculates the location of the mobile station. Due to the use of the differential positioning principle, the common error between the base station and the mobile station is eliminated, and the positioning accuracy is greatly improved. If carrier phase differential is used, the positioning accuracy can reach the cm level, and if pseudo-range differential is used, the positioning accuracy can reach about 2m.
From the above process analysis we can see that:
- To achieve high-precision positioning through differential positioning, you need to build your own base station system. The user needs to purchase, install, and arrange the base station, and also needs to configure the base station's operation and maintenance personnel.
- The mobile station is required to be within the coverage range of the base station communication radio. Due to the influence of the earth's curvature, the transmission distance of the communication radio is generally only a dozen kilometers to 30 kilometers for ground-to-ground transmission, and 100-200 kilometers for air-to-ground transmission. If the mobile station exceeds the transmission range of the base station communication radio, it is necessary to add base stations to ensure the full coverage of the mobile station, which will increase costs and system complexity.
In the field of military applications, the method of adding base stations can be used to meet the full differential requirements of the mobile station, but in the fields of industrial use and civilian use, the method of adding base stations is more difficult.So is there a way to achieve high-precision differential positioning without building a base station system ourselves, and to break through the communication distance limitations of communication radio stations?
Yes, this is network differential . The user unit only needs one GNSS receiver as a mobile station to complete differential positioning and obtain high-precision positioning results.
Basic prinpicles of CORS network differentiation
CORS (Continuously Operating Reference Stations) is a continuously operating network reference station that sends and receives GNSS differential data through the network. After users visit a CORS station, they can achieve differential positioning of a GNSS mobile station without setting up a separate GNSS base station.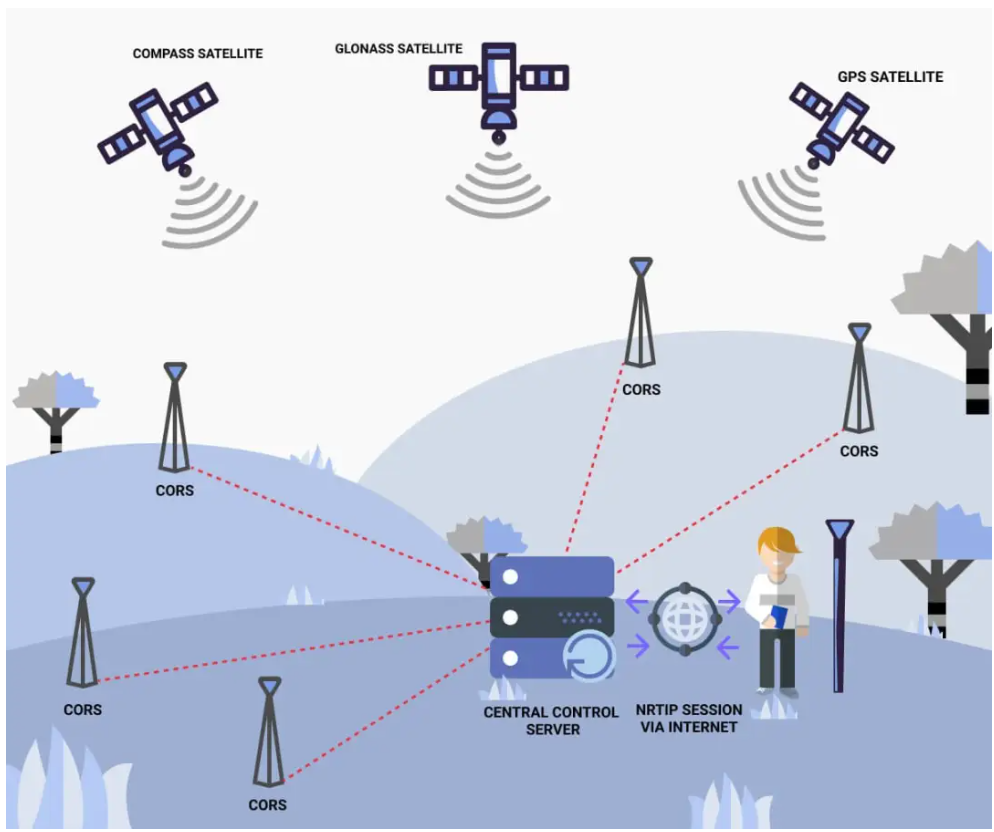
The core part of the CORS-based network differential consists of multiple reference stations and a data processing center. Multiple reference stations are deployed in a certain area, and the reference stations are distributed in a mesh. Since the reference stations are fixed, they can be connected to each other through the ground Internet.
The observation information of the reference station is transmitted to the data processing center in real time through the network. The data processing center uses the precisely known coordinate position of the reference station to model the errors such as the ionosphere, the process, and the orbit error within the network range, and generates the observation information required by the mobile station in real time, and broadcasts this observation information to the mobile station in a certain data format.
After receiving the observation information, the mobile station completes the differential positioning, thereby improving the accuracy of GNSS positioning.
The distance between ground reference stations is generally determined according to specific application requirements and geographical environment. Generally speaking, the distance between stations is usually between a dozen and several hundred kilometers, within which the relationship between coverage and positioning accuracy can be balanced. Closer stations can provide higher accuracy but smaller coverage, while farther stations can expand coverage but may reduce accuracy.
Generally speaking, in densely populated urban areas where high-precision positioning is required, the distance between CORS stations is shorter, while in rural areas, deserts and other areas, the distance between CORS stations is longer.
In actual applications, the distance between sites will be optimized based on factors such as terrain, signal propagation characteristics, and user needs to ensure that the system can provide the required positioning accuracy and coverage.
Network differential based on CORS station does not require the construction of base stations by itself, and can break through the distance limit of communication radio stations. However, there are two problems here:
- What is the communication link between the data processing center and the mobile station?
- What is the source of the observations?
Communication links in network differentiation
Network differentiation uses mobile communication networks (3G, 4G) or terrestrial Internet as communication links, and the communication is bidirectional.
The data processing center broadcasts the observation information through the mobile communication network or the ground Internet;
The mobile station sends its location information to the data processing center via the mobile communication network or the terrestrial Internet;
Sources of Observations in Network Difference
In CORS network differentiation, how is the observation information required by the mobile station generated?
The mainstream technology currently used in CORS network differential is virtual reference station technology (VRS). The mobile station sends its own single-machine positioning results to the data processing center through the network. After receiving the location of the mobile station, the data processing center finds several reference stations near the location. The data information of these reference stations is used to model the ionospheric delay and tropospheric delay at the location of the mobile station, and an observation data is calculated and generated. This generated observation data is then sent to the mobile station through the network.
This observation data is not the data of a real reference station, but the data of a "virtual" reference station generated by software. The coordinates of this reference station are the coordinates sent by the mobile station to the data processing center.
Because this coordinate point does not actually exist but is calculated and virtual, the technology is called Virtual Reference Station Technology (VRS).
Domestic institutions providing network differential services
There are many organizations in China that provide network differential services. The private companies that provide commercial services mainly include Qianxun, Liufen, etc. These companies have built their own CORS station ground-based augmentation systems across the country, and have built their own location servers to provide commercial location services. After users register an account and purchase services, they can log in to the location server and obtain virtual observation data for differential from the location server according to the network differential protocol.
Network Differentiation Accurary
The accuracy of network differential depends on the data accuracy of the differential service provider. If the organization has more and denser sites, a wider coverage area, and a more complete algorithm in the data processing center, the accuracy of network differential will be high.
In addition, network differential service providers will provide services of different precisions, ranging from meter level to mm level. The charges for services of different precisions are different, and users can choose according to their actual situation. For example, the services of Qianxun Company with different precisions are as follows:
Network Differential Protocol
NTRIP (Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol) is one of the mainstream communication protocols of the CORS system. NTRIP transmits differential GNSS data through the Internet, providing users with a real-time, high-precision differential positioning solution suitable for various application scenarios that require high-precision positioning.
NTrip protocol is a network protocol based on TCP.
There are many client softwares on the market that support the NTRIP protocol. Through the client software, you can directly log in to the location server of a commercial organization and obtain virtual observation information.
Register and log in to the location server
Here we take Qianxun server as an example. Register an account on Qianxun official website, select the required service type and usage time according to the positioning accuracy requirements, and after payment, Qianxun platform will assign an account and password. Then record the domain name (or IP address), port number, Mountpoint/source/mount point and other information of the location server.
The information of Qianxun location server is as follows:
1) Address
Domain name: rtd.ntrip.qxwz.com or IP (60.205.8.49)
2) Port
Port: 8001 corresponds to ITRF2008 coordinate system
Port: 8002 corresponds to WGS84
Port: 8003 corresponds to CGCS2000
3)Mountpoint/Source/Mount point
RTCM32_GGB or RTCM23_GPS
Log in to the location server using NtripClient
The system connection diagram is as follows:
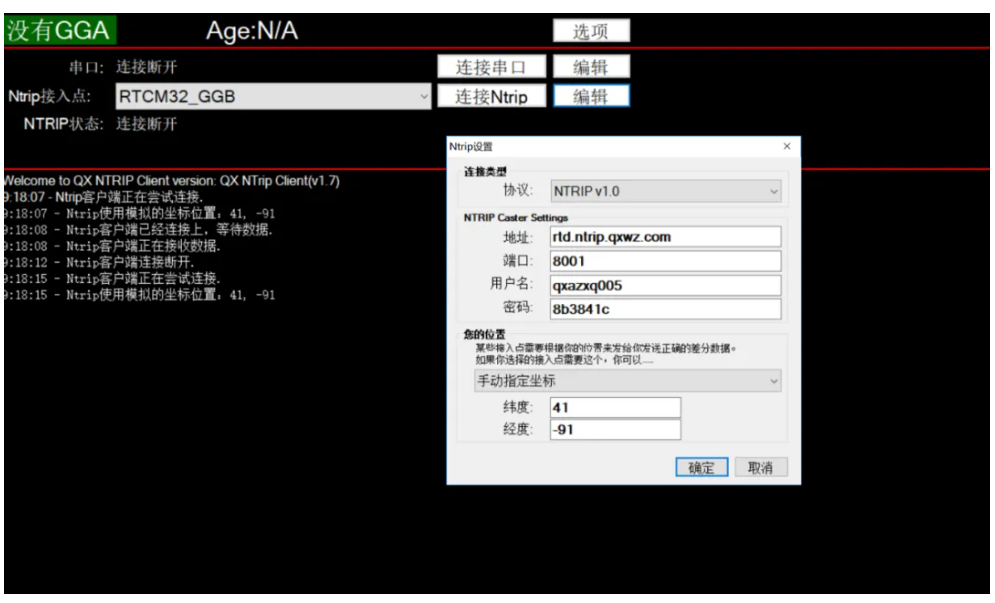
- NtripClient software is easy to operate. You can set the domain name address, port number, mount point, account password, etc. on the interface. Then click "connect". The software will automatically connect to Qianxun's location server.
If the mobile station is fixed, you can enter your approximate location in "My Location" on the interface;
If the mobile station is mobile, connect the serial port of the mobile station GNSS receiver to the computer. The GNSS receiver outputs the $GGA statement in the NEMA0183 protocol to the NtripClient client. Then the NtripClient client will send the position of the GNSS receiver to the Qianxun location server at a certain frequency according to the NTRIP protocol.
NtripClient software receives VRS observation data sent by the location server, parses the Ntrip differential protocol, and converts it into RTCM differential observation data. The RTCM observation data can be saved to disk or output from the computer's serial port.
Through the computer's serial port, the RTCM differential observation data is continuously output to the GNSS receiver, and the GNSS receiver completes the real-time differential positioning.
If the mobile station is not convenient to use a computer and cannot run the NtripClient client , we need to develop an embedded platform ourselves to implement the functions of the NrtipClient client. There are open source codes on the Internet that can be implemented.
The network between the mobile station and the location server can utilize the terrestrial Internet or the 4G mobile Internet.