The positioning system based on Beidou-GPS satellites has penetrated into various industries in the country, from the in-car map navigation to the national military field. It can be said that the Beidou-GPS satellite positioning system has become an indispensable part of human modern life.
Due to the long distance between the satellite and the earth, the navigation satellite is generally about 22,000 km away from the earth's surface. After the signal transmitted from the satellite reaches the ground after a long distance of propagation, the signal is already very weak.
If there are other high-power signals near the satellite positioning terminal, it will cause serious interference to the Beidou-GPS satellite signal, resulting in a decrease in the number of satellites received by the satellite positioning terminal, poor positioning accuracy, and even failure to position normally.
The emergence of anti-interference antennas is to solve the above problems. It can ensure that the satellite positioning terminal can be positioned normally under the condition of interference signals around. Since the frequency, power, quantity and type of interference signals in reality vary greatly, some are unintentional interference and some are intentional interference, different interference scenarios require different anti-interference antennas. In the spirit of scientific objectivity, it is impossible for an anti-interference antenna to adapt to all interference scenarios.
**Anti-interference antennas can only suppress interference in certain types of interference scenarios .
The anti-interference antenna processes the signals (including satellite signals and interference signals) received, removes the interference signals, and outputs the processed signals to the satellite positioning receiver, which outputs the location information after calculation. The specific composition diagram can be seen in the figure below.
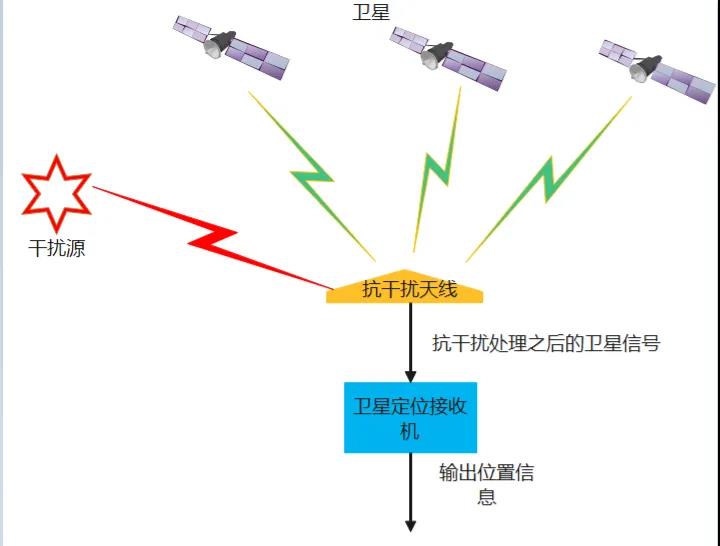
Several parameters that need to be considered when selecting an anti-interference antenna are:
1. Interference frequency
2. Number of Interferences
3. Interference Type
4. Anti-interference ability
5. Anti-burning power
6. Interface control
Interference signal frequency
According to the relationship between the frequency of the interference signal and the frequency of the satellite signal, the interference signal can be divided into out-band interference and in-band interference. Out-band interference means that the interference signal frequency is outside the frequency band of the satellite signal, and the interference signal frequency band and the satellite signal frequency band do not overlap. In-band interference means that the interference signal frequency band and the satellite signal frequency band overlap.
Since out-of-band interference has little effect on satellite signals, anti-interference antennas are mainly aimed at in-band interference signals, and certain measures are taken to suppress or reduce the impact of in-band interference signals on satellite positioning.
There are currently four major global satellite navigation and positioning systems: China's Beidou Navigation and Positioning System, the United States' GPS system, Europe's Galileo system, and Russia's GLONASS system. The frequencies of the signals transmitted by satellites in each positioning system are different. The frequencies of the four satellite navigation and positioning systems can be seen in the table below.
It is impossible for an anti-interference antenna to achieve anti-interference for all satellite signal frequency bands. Therefore, when selecting an anti-interference antenna, the first thing to determine is which satellite navigation system and which frequency band of the interference signal to be processed for anti-interference. The more common anti-interference antennas in China include:
The anti-interference antenna for Beidou B3 frequency for military users can suppress interference signals within the Beidou B3 frequency band;
The anti-interference antenna for GPS L1 and BeiDou B1 frequency points for civilian users can suppress interference signals in the GPS L1 and BeiDou B1 frequency bands;
Number of interference signals Anti-interference antennas can only suppress a certain number of interference signals, so when selecting an antenna, you must determine how many interference signals need to be suppressed. The number of interference signals is related to the number of antenna elements used. Assuming the number of antenna elements is N, N-1 interference signals can be suppressed.
There are two types of antennas commonly used in the industry, namely 4-element antenna and 7-element antenna. The 4-element antenna can suppress 3 interferences, and the 7-element antenna can suppress 6 interferences.
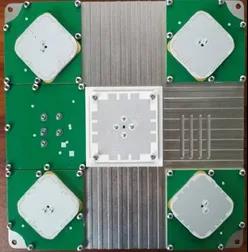
The following is a layout diagram of a common 4-element anti-interference antenna. The four corners of the square are the antennas for the Beidou B3 frequency band, and the antennas for GPS L1 and Beidou B1 are installed in the middle. This antenna can suppress interference from the three Beidou B3 frequency bands, while also being able to receive GPS L1 and Beidou B1 satellite signals normally. The antenna does not suppress interference within the GPS L1 and Beidou B1 signal bands.
Common types of interference signals include: broadband interference, narrowband interference, swept frequency interference, pulse interference, etc.
Narrowband interference: According to the industry's commonly accepted standards, when the bandwidth of the interference signal is ≤ 10% of the satellite signal bandwidth, the interference signal is called narrowband interference. For example, the signal bandwidth of the Beidou B3 frequency point is 20MHz, and the bandwidth of the narrowband interference signal is ≤ 2MHz.
Broadband interference: The bandwidth of the interference signal is equivalent to the bandwidth of the satellite signal. When testing, the bandwidth of the interference signal is equal to the bandwidth of the satellite signal. For example, the signal bandwidth of the Beidou B3 frequency point is 20MHz, and the bandwidth of the broadband interference signal is 20MHz.
Anti-interferentce ability
Anti-interference capability refers to the ability of satellite positioning equipment to locate normally when the power of the interference signal increases to a certain value. The power of the interference signal at this time is the anti-interference capability of the anti-interference satellite positioning product.
The industry often uses the interference-to-signal ratio indicator to measure anti-interference capabilities. The interference-to-signal ratio, as the name implies, is the ratio of the interference signal power to the satellite signal power. According to the official documents of various satellite navigation and positioning systems, the signal power that can be guaranteed by the satellite signal reaching the ground is ≥130dBm, so -130dBm is often used as the satellite signal power in the industry. Therefore, the interference-to-signal ratio is the ratio of the interference signal power to -130dbm.
For example, the anti-interference capability of a Beidou B3 anti-interference antenna is expressed as: the interference-to-signal ratio is not less than 100dB (reference signal strength -130dBm);
Since -130dBm+100=-30dBm, the above indicator means that when the power of the interference signal is not greater than -30dBm, the Beidou B3 anti-interference positioning product can position normally.
The anti-interference antenna works in an interference environment. If the power of the interference signal is too strong, it may exceed the tolerance range of the anti-interference antenna, thus causing permanent damage to the anti-interference antenna. Therefore, the anti-interference antenna needs to provide an indicator of anti-burning power. The meaning of this indicator is: when the power of the interference signal reaching the surface of the anti-interference antenna is greater than this indicator, the anti-interference antenna may be damaged. Therefore, in actual applications, it should be ensured that the power of the interference signal is less than this indicator.
The external data interface of the anti-interference antenna is used to monitor the antenna. The status information output by the anti-interference antenna includes: the number of interferences and the direction of interference; the control instructions sent to the anti-interference antenna include: controlling whether the current mode is direct mode or anti-interference mode. If the direct mode is selected, the antenna is directly connected to the back-end satellite receiver without anti-interference algorithm processing.
There are generally no rigid requirements for the external interface protocol and content of the anti-interference antenna. Users can communicate further with the manufacturer according to their needs, and the manufacturer will complete the interface input and output protocol.
Anti-interference antenna composition
The following uses the Beidou B3 anti-interference antenna as an example to explain the system composition of the antenna. The composition of other types of anti-interference antenna products is similar.
The anti-interference antenna is composed of an array antenna, a low-noise amplifier circuit, a related receiving channel, a signal processing circuit, an up-conversion circuit and a power supply unit.
The antenna array receives Beidou B3 band satellite signals. The number of antenna arrays can be 4, 7 or other numbers;
The receiving channel group performs low-noise amplification, filtering, and down-conversion on the Beidou B3 frequency band signal received by the antenna, converting it into a signal suitable for AD sampling;
The signal processing module converts the analog intermediate frequency signal into a digital signal, processes it in the FPGA to complete the anti-interference function, and converts the processed signal into an analog intermediate frequency signal;
The modulator modulates the analog intermediate frequency signal to the original carrier frequency, and selects one output path through the switch together with the low-noise amplified Beidou B3 band signal (through signal);
The power conversion module converts the input DC voltage into a voltage suitable for the operation of each module chip.
Summarize
Anti-interference antennas can be considered comprehensively from multiple aspects such as interference frequency, type, quantity, anti-interference ability, anti-burning power and interface control. In addition, there is another most important point when selecting products:
Acceptable installation space and structural dimensions!!! The structural size of the antenna has a great influence on the layout of the anti-interference antenna array and will also limit the anti-interference capability of the antenna.
The selection of anti-interference antennas needs to consider multiple factors, make compromises and balances among various performance indicators, and finally determine the indicators of the anti-interference antenna to achieve the purpose of optimization.